"A key consideration preparing for an IPO is to ensure the readiness of a company"s financial function and to reinforce the confidence of existing and future (prospective) owners in its financial performance"
PART 3. ACCOUNTING ASPECTS OF LAUNCHING IPO ON MOSCOW EXCHANGE
The success of an initial public offering (IPO) depends on the combination of two factors: attractive valuations and the company's preparedness to launch when the window of opportunity opens. While market conditions are an external factor that is hard to influence, IPO readiness depends fully on the company. Preparing for an IPO is a complicated, multifaceted process that focuses on establishing proper corporate governance, building a robust financial function capable of presenting financial statements in accordance with listing requirements, and delivering a compelling equity growth story to investors. It is also critical to understand that an IPO is only the beginning of life as a public company, which has to comply with increased requirements for corporate conduct and governance, business transparency, and timely and fair reporting after the IPO.
One of the key questions companies ask when considering going public is: "What kind of financial statements do we need?" The answer may prove more difficult than it seems. Apart from regulatory requirements, which may be inconsistent or even conflicting, market practices also vary across IPO destinations, requiring considerable adjustments to the IPO preparation process.
Chapter 1. Overview of Russian Legislation
Securities issuance and trading is governed by Federal Law No. 39-FZ, On the Securities Market (hereinafter, the Securities Market Law).
Currently, the Disclosure Regulation (as amended by Order of the Federal Service for Capital Markets No. 12-27/pz-n dated 24 April 2012) governs, to the extent that it does not contradict federal law, the scope, timeframes and procedures for the statutory disclosure obligations of public companies (issuers), disclosure obligations that they should fulfil at each stage of the listing process, and their specific disclosures, such as a prospectus, summarised (consolidated) financial statements, quarterly reports and material event notices. The Disclosure Regulation also sets forth the requirements for issuers to disclose other information related to their obligations and rights with respect to the securities offered or being offered.
Requirements for the preparation, presentation and publication of consolidated financial statements by legal entities organised under the laws of the Russian Federation are outlined in the Consolidated Financial Statements Law and the Securities Market Law (see the abbreviations of laws and regulations).
Chapter 2. Financial Information Disclosure Requirements
1. Annual and interim financial statements
According to Article 22.2 of the Securities Market Law, a prospectus should contain, among other things, financial statements and other financial information of the issuer, including:
- Annual financial statements for the previous three reporting years;
- Interim financial statements for the latest full reporting period covering three, six or nine months;
- Consolidated financial statements for the previous three reporting years;
- Consolidated financial statements for the latest full reporting period covering six months
Annual and interim financial statements (hereinafter, "annual RAS financial statements" and "interim RAS financial statements", respectively) should be prepared in accordance with the Accounting Law and the Accounting Regulations as approved by the relevant orders of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
According to Article 30.4 of the Securities Market Law, issuers registering their prospectus or admitting their Russian Depository Receipts to trading on a regulated market where admission requires filing a prospectus must publish consolidated financial statements when the listing begins or, if provided for by the prospectus, after its registration or after the admission of their Russian Depository Receipts to trading on a regulated market.
Issuers must prepare their consolidated financial statements in accordance with federal laws and other regulations of the Russian Federation, specifically the Consolidated Financial Statements Law.
As set forth in Article 3 of the Consolidated Financial Statements Law, such financial statements must be prepared in accordance with IFRS (hereinafter, "annual IFRS consolidated financial statements"), with the Russian Government recognising IFRS (standards and interpretations) as approved by the IFRS Foundation and recognised as prescribed by Russian Government Decree No. 107 dated 25 February 2011, On the Approval of Regulations for Recognising International Financial Reporting Standards and Interpretations of International Financial Reporting Standards for their Application in the Russian Federation.
Similar requirements for the preparation and presentation of consolidated financial statements are set forth in Section 7 of the Disclosure Regulations.
Given the above information, the issuer must publish (disclose in its prospectus) annual RAS financial statements and annual IFRS consolidated financial statements for the previous three full reporting years. If the issuer has been in existence less than three years, it must prepare and disclose annual RAS financial statements and annual IFRS consolidated financial statements for each full reporting year.
Interim RAS financial statements are filed for the latest full reporting period covering three, six or nine months. At the same time, according to Russian legislation, interim IFRS consolidated financial statements must be filed only for the latest full reporting period covering six months (financial statements for the six-month period). In other words, there are no formal requirements for filing interim quarterly IFRS consolidated financial statements (covering the first quarter/three months or/and the third quarter/nine months).
However, if a company prepares interim quarterly consolidated financial statements in accordance with IFRS (e.g., pursuant to the founding documents as prescribed by Article 4.2 of the Consolidated Financial Statements Law) and presents such financial statements to participants (including shareholders), it should, we believe, include such interim IFRS consolidated financial statements for the relevant reporting periods (the first quarter/three months or the third quarter/nine months) in the prospectus.
RAS and IFRS financial statements must be prepared in the Russian language.
To the extent that the disclosure of financial statements is required by the Disclosure Regulations, such financial statements must be prepared in accordance with IFRS or other internationally recognised financial statements.
2. Scope of financial information included in a prospectus
The Disclosure Regulations contain detailed requirements for the scope of financial information that must be included in the prospectus. Apart from financial statements prepared in accordance with RAS and IFRS, issuers must provide extensive financial information and analytics about their operations. Pursuant to the Disclosure Regulations and common practice, a prospectus for an IPO on the Moscow Exchange is filed using the form set out in Appendix 2 of the Disclosure Regulations.
Information about the issuer's financial and operating performance (Section 5 of the Standard Prospectus Form) must be disclosed for the previous five full fiscal years or, if the issuer has been in existence less than five years, for each full fiscal year.
Currently, issuers generally disclose RAS (non-consolidated) financial information in their prospectus unless otherwise expressly provided for in Russian legislation. However, information for Section 5 of the Standard Prospectus Form (Appendix 2 of the Disclosure Regulations) may be prepared by the issuer in accordance with IFRS.
3. Statutory audit of financial statements
Annual RAS financial statements and annual IFRS consolidated financial statements for each reporting period must be included in the prospectus together with an independent auditor"s report on the same financial statements.
In the event that the interim RAS and/or IFRS financial statements are audited, as may be required by participants, shareholders, lenders or other persons as well as by Russian legislation, the issuer should also provide such financial statements together with the auditor's report.
If the filing date of the financial statements for the first reporting year has not expired, the issuer must include interim financial statements in the prospectus, and if the filing date of quarterly financial statements has not expired on the approval date of the prospectus, the issuer must engage an auditor to audit its opening financial statements and file such financial statements together with an auditor's report.
If the filing date of the annual financial statements for the first reporting year has not expired on the approval date of the prospectus, the issuer must engage an auditor to audit its quarterly financial statements and file such financial statements together with an auditor's report.
The issuer's annual financial statements and/or summarised (consolidated) financial statements must be audited by an auditor, and the auditor's report must be filed together with such annual financial statements and annual summarised (consolidated) financial statements.
The following table summarizes the financial information that must be disclosed according to the Standard Prospectus Form:
| Financial information disclosure requirements 1 | Section of Standard Prospectus Form 2 |
|---|---|
Basic information about the issuer's financial condition, including:
|
Section 3 |
Information about the issuer"s core business, including:
|
Section 4 |
Information about the issuer's financial and operating performance, including:
|
Section 5 |
Financial statements and other financial information of the issuer, including:
|
Section 8 |
Chapter 3.Preparing IPO financial information
1. The auditor's role
An auditor, along with the investment bank and legal counsel, advises the issuer with regards to preparation for an IPO.
Under current Russian legislation governing the securities market, the issuer must include annual RAS financial statements and annual IFRS consolidated financial statements for each reporting year in the prospectus together with an independent auditor's report on such financial statements (for details, see Chapter 1 above).
An auditor issuing an audit report on financial statements that are included in the prospectus and persons signing or approving the prospectus (by voting) jointly bear subsidiary liability for potential damages that may be caused by the issuer to the investor and/or the holder of securities through the presentation of false, incomplete and/or misleading information in the prospectus approved by them.
According to auditing standards, the auditor must review the prospectus to identify possible significant inconsistencies with the audited financial statements or, in other words, identify information that may conflict with the audited financial statements.
To comply with this requirement, the auditor must, as a minimum, read the prospectus and perform certain procedures, including a review of the prospectus, an analysis of subsequent events, interviews with the issuer's management, and other procedures as applicable.
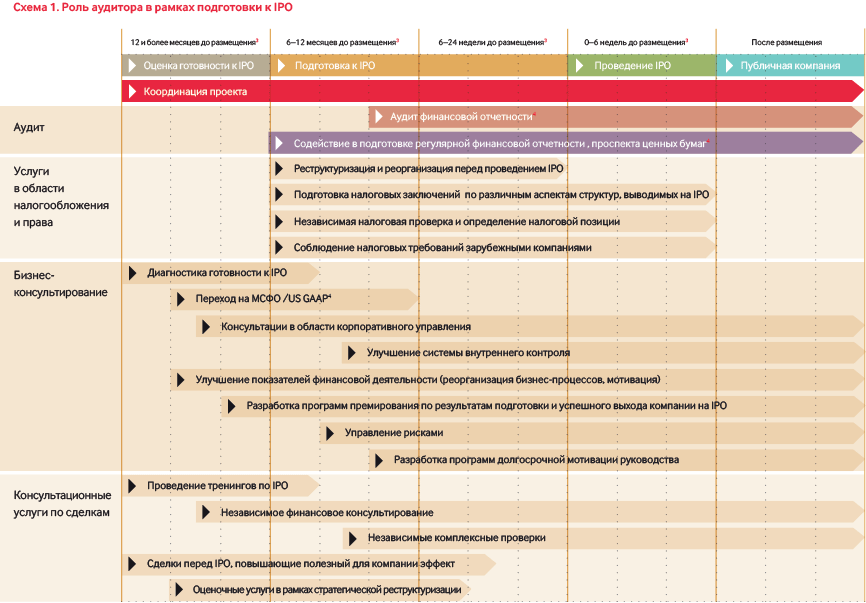
The following chart summarises a standard IPO process, including areas where the auditor may be involved.
2. Preparing financial information for a prospectus
Financial information included in the prospectus must comply with Russian legislation and should convey a compelling equity story for potential investors. The scope of disclosures depends on applicable legislation, the nature of the issuer's business, market practices, and recommendations provided by the investment bank.
It is essential to define early the list of necessary information and to perform thorough diagnostics to identify its availability, the capabilities of the financial function to collect, verify and analyse it, and the need to hire external advisors to cope with pressing IPO deadlines. To prepare a transparent and straightforward investment case, the issuer should make a timely decision on how to present its track record on growth. The historical performance data should be correct, comparable between periods, and consistent with financial statements, while the basic metrics should be calculated in accordance with Russian legislation.
Normally, the proper preparation and review of this information requires considerable effort from the financial function, close interaction with other functions, and the involvement of both the business and external specialists. The issuer should plan early and well, distribute roles and responsibilities within the company, and define areas of accountability for external advisors.
3. Risks associated with investing in an IPO
As outlined above, both an in-depth analysis of the risks associated with investing in securities and the issuer's risk management policies comprise an essential part of the prospectus.
An analysis of financial risks is very important. It focuses on:
- The issuer's exposure to the volatility of interest rates and exchange rates arising from its operations or hedging instruments that the issuer uses to mitigate the negative effects of these risks;
- The issuer's exposure to currency risk with respect to its financial condition, liquidity, financing sources and financial results;
- An action plan for minimising the negative effects of fluctuations in exchange rates and interest rates on the issuer's operations;
- The potential effects of inflation on returns from securities (the prospectus should contain inflation expectations and an action plan to mitigate this risk);
- A summary of financial results that are most vulnerable to the mentioned financial risks (the prospectus should disclose the risks involved, the likelihood of each risk event and the effects on financial statements);
When analysing non-financial risks, it is critical to remember that they may also affect the issuer"s financial condition and financial results, and as such should be disclosed in the summary of the financial risk analysis.
Chapter 4. Preparing and Publishing Post-IPO Financial Information (Quarterly Reports)
Companies should analyse post-IPO disclosure requirements early, before going public. Studying the relevant regulations, market practices and experiences of other public companies is essential.
The publication dates for regular reports are established by Russian legislation and the regulations of the stock exchange; non-compliance may affect the company"s market capitalisation, trigger Delisiting procedures, or worse – lead to penalties. According to Chapter 7 of Article 30 of the Securities Market Law and clauses 2.5.16 and 5.12 of Order of the Federal Financial Markets Service No. 11-46/pz-n, the issuer must disclose the following information on the securities market after the listing:
- Quarterly reports;
- Consolidated financial statements;
- Material event notices, which may have a significant impact on the valuations after their publication;
- For details, see ( Part 2. ) Listing Rules – International Best Practice, Chapter 4. Obligation to Disclose Information .
Quarterly reports are prepared for each quarter to present information as of the end of the reporting period. Such reports should be published online within 45 days following the end of the relevant quarter. They should be available online for five years after the publication date.
The quarterly report for the initial quarter includes the issuer"s financial statements for the latest full reporting year, the auditor"s report on the same financial statements, and the issuer"s interim financial statements for the latest full reporting period covering the first three months of the reporting year. The quarterly reports for the second and third quarters include the issuer"s interim financial statements for the latest full reporting periods covering the first six and nine months of the reporting year, respectively. The quarterly report for the fourth quarter does not include any financial statements.

